Understanding the world of chemistry can sometimes feel like deciphering a foreign language. But knowing a few key terms can make a big difference, especially if you’re diving into topics like dispersants and surfactants. These terms often pop up in industrial applications, household products, and even environmental cleanups. But what exactly sets them apart? Let’s break it down in a way that’s easy to understand.
What is a Dispersant?
A dispersant is a chemical agent used to break up and distribute particles or droplets in a liquid. Think of it as the mediator in a conflict, separating clumps of particles that would otherwise stick together. When you mix a dispersant into a solution, it helps suspend tiny particles throughout the liquid, preventing them from settling at the bottom.
How Do Dispersants Work?
Dispersants work by attaching to the surface of particles and reducing the forces that cause them to clump together. This process helps evenly distribute the particles throughout the liquid, keeping them apart and stable. For example, in paints, dispersants keep pigments evenly distributed, ensuring a smooth and consistent finish.
Common Uses of Dispersants
Dispersants are widely used in various industries:
Oil spill cleanup: Dispersants help break down oil slicks, allowing microbes to more easily digest the oil.
Paints and coatings: Used to keep pigments and fillers evenly distributed.
Pharmaceuticals: Helps in the distribution of active ingredients.

Dispersant NNO (B)
What is a Surfactant?
A surfactant, on the other hand, is a substance that lowers the surface tension between two liquids or a liquid and a solid. Imagine a surfactant as a diplomat who encourages two opposing sides to come together, making it easier for them to mix. Surfactants are often used as detergents, wetting agents, emulsifiers, and foaming agents.
How Do Surfactants Work?
Surfactants have two ends: one that is attracted to water (hydrophilic) and another that is attracted to oil or grease (hydrophobic). This unique structure allows surfactants to surround greasy dirt and pull it away from surfaces when rinsed with water.
Common Uses of Surfactants
Surfactants are commonly found in:
Household cleaning products: Such as dish soaps and laundry detergents.
Personal care products: Like shampoos and body washes.
Agricultural sprays: Used to help pesticides spread evenly over crops.
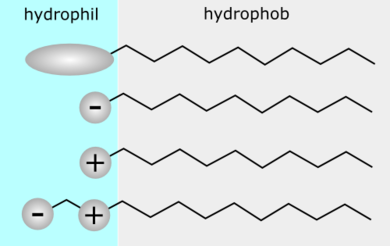
image from wikipedia
Key Differences Between Dispersants and Surfactants
Primary Function Comparison
Dispersants are mainly used to break up and stabilize particles within a liquid, preventing them from settling.
Surfactants primarily reduce surface tension, allowing two different substances (like oil and water) to mix more easily.
Mechanism of Action Differences
Dispersants work by attaching to particles, providing a barrier that keeps them separate.
Surfactants work by surrounding particles, allowing them to be carried away in a solution.
Applications in Various Industries
While both dispersants and surfactants are used across a variety of industries, their specific roles differ:
Dispersants are favored in situations where preventing particle clumping is essential (e.g., paint manufacturing).
Surfactants are often used in cleaning and emulsifying tasks (e.g., making shampoos lather or keeping salad dressings mixed).
Chemical Composition of Dispersants and Surfactants
Typical Components in Dispersants
Dispersants are usually composed of molecules with functional groups that can interact with the surface of particles, aiding in their separation.
Typical Components in Surfactants
Surfactants contain both hydrophilic and hydrophobic groups, giving them the ability to interact with water and oil simultaneously.
How Dispersants and Surfactants Work
How Dispersants Work: Breaking Down Particles
When dispersants are added to a mixture, they coat the surface of particles, reducing their tendency to clump together. This helps keep particles evenly distributed, enhancing the stability of the mixture. For instance, in concrete mixing, dispersants ensure that fine particles are uniformly distributed throughout the mixture, improving its flow and strength.
How Surfactants Work: Lowering Surface Tension
Surfactants reduce the surface tension of water, allowing it to spread and wet surfaces more effectively. In cleaning, this means dirt and oils can be lifted and washed away with ease. Picture a surfactant as a hand that gently peels away the sticky mess clinging to your dishes.
Applications of Dispersants and Surfactants
Dispersants in the Oil Industry
The oil industry relies heavily on dispersants, especially during oil spills. When oil spills into the ocean, dispersants help break it into smaller droplets, making it easier for natural processes to degrade the oil. However, dispersants don’t eliminate the oil; they just help it disperse more evenly in the water.
Benefits and Limitations
Benefits: Speeds up the natural breakdown of oil, reduces the impact on the shoreline.
Limitations: Can have environmental side effects, such as toxicity to marine life.
Surfactants in Household Products
Surfactants are the magic behind many everyday products. From foaming shampoos to dish soaps that cut through grease, they make cleaning easier and more effective.
Examples of Surfactants in Personal Care Items
Shampoos use surfactants to create lather, helping to lift dirt and oil from the scalp. Body washes use them to remove sweat and impurities, leaving skin feeling fresh.
Industrial Uses of Dispersants
In industries like paint and coatings, dispersants prevent pigment clumping, ensuring a smooth and consistent product. In pharmaceuticals, they help distribute active ingredients evenly.
Industrial Uses of Surfactants
Surfactants are key in textile manufacturing, where they aid in dyeing fabrics by allowing the dye to penetrate the fibers evenly. They are also used in agriculture to help pesticides spread across crops more effectively.
Dispersants and surfactants may seem similar, but they serve different functions. Dispersants break up particles and keep them stable, while surfactants reduce surface tension and help substances mix. Choosing the right one depends on the specific needs of the task. Understanding their differences ensures you can select the most suitable agent for the job.

 English
English 





