What is the difference between melamine and formaldehyde?
Navigating the world of chemical compounds can feel like diving into a complex maze. Two names that often pop up in industrial and manufacturing settings are melamine and formaldehyde. Although they are frequently used together, they have distinct properties and applications. Let's dive deeper into understanding what sets these two chemicals apart and how they play different roles across various industries.
What is Melamine?
Melamine is an organic compound with the chemical formula C3H6N6. It is a nitrogen-rich substance, often recognized for its white, crystalline powder appearance. Melamine’s nitrogen content makes it a valuable ingredient in the production of plastics, laminates, and certain types of dinnerware. It also finds use in flame retardants and fertilizers due to its chemical stability.
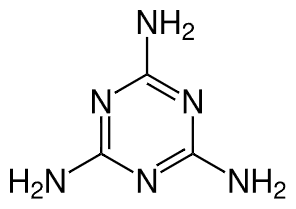
What is Formaldehyde?
Formaldehyde is a colorless, pungent gas with the chemical formula CH2O. It is known for its strong smell and is one of the simplest forms of aldehydes. Formaldehyde is commonly used as a disinfectant, preservative, and adhesive component. Its ability to cross-link with proteins and other compounds makes it a valuable ingredient in the production of resins, which are then used to create durable products like particleboard and plywood.
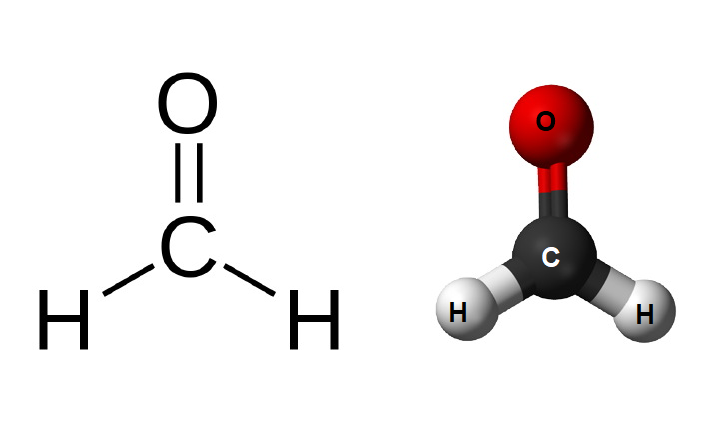
Chemical Structure of Melamine and Formaldehyde
Chemical Structure of Melamine
Melamine’s structure consists of a triazine ring with three amino groups attached. This configuration makes it highly stable, resistant to heat, and able to form complex structures. The nitrogen atoms in melamine contribute to its flame-retardant properties, which are useful in various applications requiring fire resistance.
Chemical Structure of Formaldehyde
Formaldehyde’s structure is much simpler, with a single carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom and single-bonded to two hydrogen atoms. This simplicity makes it highly reactive, allowing it to form polymers and other compounds with relative ease. Its reactive nature is what makes formaldehyde so valuable in the production of resins and other cross-linking materials.
Production Processes
Melamine is produced through a process called condensation of urea, which involves heating urea to release ammonia and create melamine. This method is widely used in industrial settings due to its efficiency and relatively low cost.
Formaldehyde is produced by oxidizing methanol, typically using a metal catalyst. The resulting formaldehyde gas can then be converted into a liquid solution for use in various applications.
Applications of Melamine and Formaldehyde
Applications of Melamine
Melamine finds its way into a host of products:
Construction Materials: It is used in laminates for countertops and cabinets.
Dinnerware: Melamine-based plastics create durable and shatter-resistant dishes.
Flame Retardants: Due to its high nitrogen content, it is used to make materials more fire-resistant.
Industrial Coatings: Melamine resins are often found in coatings that need to withstand wear and tear.
Applications of Formaldehyde
Formaldehyde has a broad range of uses, from adhesives and disinfectants to preservatives and coatings:
Resin Production: It is a key ingredient in making urea-formaldehyde and phenol-formaldehyde resins, which are used in particleboard and plywood.
Healthcare: It serves as a disinfectant in hospitals and as a preservative in laboratories.
Textile Industry: Formaldehyde is used to create wrinkle-resistant fabrics.
Melamine-Formaldehyde Resin
Interestingly, melamine and formaldehyde are often combined to create melamine-formaldehyde resin, a tough, durable plastic used in high-pressure laminates and molding compounds. This resin is known for its heat-resistant and hard-wearing properties, making it ideal for products that need to withstand frequent use.
Differences in Physical Properties
While melamine and formaldehyde are both versatile, they differ significantly in physical form:
Melamine is a solid powder, making it ideal for creating molded products or laminates.
Formaldehyde is a gas at room temperature, although it is commonly sold as a liquid solution. Its strong odor and reactive nature set it apart from the solid-state stability of melamine.
Differences in Chemical Properties
The reactivity and stability of melamine and formaldehyde differ greatly:
Melamine is relatively stable, with low reactivity, making it suitable for applications where chemical stability is crucial.
Formaldehyde is highly reactive, easily forming bonds with other compounds, which makes it effective for producing adhesives and resins.
How to Choose Between Melamine and Formaldehyde
Choosing between melamine and formaldehyde depends on the application:
For durable, heat-resistant materials, melamine is often the better choice.
For adhesives, disinfectants, or resins, formaldehyde’s reactivity makes it the go-to option.
While melamine and formaldehyde may often be found together in products like melamine-formaldehyde resin, they serve different roles in the world of chemistry and manufacturing. Melamine brings stability, durability, and fire resistance to the table, while formaldehyde offers reactivity and versatility in creating adhesives and resins. Understanding these differences helps in making informed decisions when selecting materials for various projects.
Recommended Products
Related News About Construction Chemicals

 English
English 




